종목토론카테고리
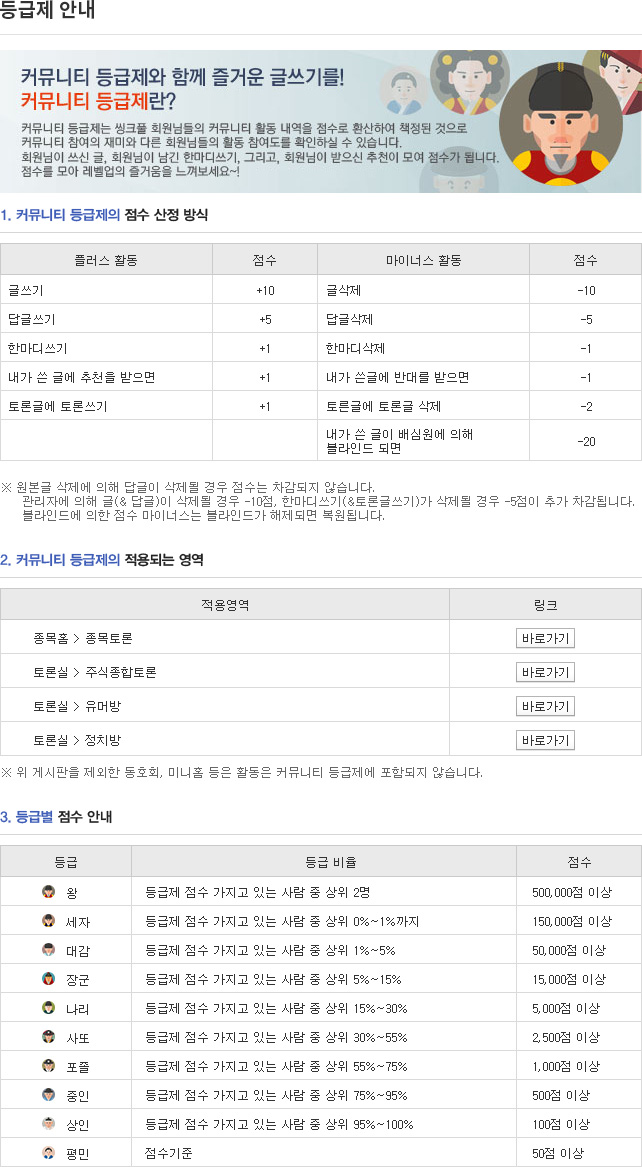
게시판버튼
게시글 제목
휴젠 기사게시글 내용
December 16, 2021
Lenzilumab improves survival without ventilation in patients hospitalized with COVID-19
Lenzilumab은 COVID-19로 입원한 환자들의 인공호흡 없이 생존을 개선합니다.
Lenzilumab significantly improved survival without the need for invasive mechanical ventilation among patients hospitalized with COVID-19, according to results of the LIVE-AIR trial published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
The safety profile of lenzilumab was similar to that of placebo, researchers reported.

“Lenzilumab is a novel anti-human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor monoclonal antibody that directly binds granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, with high specificity and affinity, and a slow off-rate to prevent signaling through its receptor,” Zelalem Temesgen, MD, infectious disease specialist in the division of infectious diseases at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, and colleagues wrote. “It has shown efficacy in clinical studies of various disease settings with no serious adverse events attributed to its administration.”
란셋 호흡기 메디신(The Lancet Respiratory Medicine)에 게재된 LIVE-AIR 시험 결과에 따르면 렌질루맙은 COVID-19로 입원한 환자들 사이에서 침습적인 기계적 인공호흡 없이 생존을 크게 향상시켰다.
연구자들은 렌질루맙의 안전 프로파일은 위약과 유사하다고 보고했다.
COVID-19 폐렴 환자를 대상으로 한 LIVE-AIR 시험에서 28일째까지 침습적 기계적 인공호흡 없이 생존이 이루어졌다.
데이터는 Temesgen Z 등으로부터 파생되었다. 2021년 랜싯 호흡기 의료진: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00494-X.
젤랄렘 테메스젠 감염병 전문의는 "렌질루맙은 과립구-대식세포 군체 자극 인자를 직접적으로 결합시키는 새로운 항인간 과립구-대식세포 군체 자극 인자로 특이성과 친화력이 높고 수용체를 통한 신호 전달을 막는 느린 속도이다"고 밝혔다.미네소타 로체스터에 있는 메이요 클리닉의 악성 질병과 동료들은 이렇게 썼다. "그것은 투여로 인한 심각한 부작용 없이 다양한 질병 환경에 대한 임상 연구에서 효과를 보여주었다."
LIVE-AIR was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial that included 479 adults with COVID-19 pneumonia (mean age, 61 years; 65% men) who did not require invasive mechanical ventilation. Patients were enrolled from May 2020 to January 2021 at 29 sites in the U.S. and Brazil. Patients were randomly assigned to receive three doses of IV lenzilumab 600 mg (Humanigen; n = 236) or placebo (n = 243) administered 8 hours apart. In addition, all patients received standard supportive care including remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead Sciences) and corticosteroids; 94% of patients received steroids, 72% received remdesivir and 69% received both.
The primary outcome was survival at 28 days without invasive mechanical ventilation. The primary outcome was achieved in 84% of patients who received lenzilumab compared with 78% who received placebo (HR = 1.54; 95% CI, 1.02-2.32; P = .04).
The incidence of invasive mechanical ventilation, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or death occurred in 15% of the lenzilumab group compared with 21% of the placebo group (OR = 0.67; 95% CI, 0.41-1.1; P = .11). Mean number of ventilator-free days was 8.8 in the lenzilumab group compared with 10.5 in the placebo group (P = .077). Mean ICU stay was 10 days for the lenzilumab group compared with 11 days for the placebo group (P = .16).
At baseline, median C-reactive protein (CRP) was 79 mg/L (77 mg/L in the lenzilumab group; 82 mg/L in the placebo group). Sensitivity analyses demonstrated that CRP levels below 79 mg/dL were associated with the greatest likelihood of survival without invasive mechanical ventilation.
“These exploratory findings might indicate the therapeutic potential of targeting a single upstream cytokine earlier in the disease process, guided by baseline CRP,” the researchers wrote.
At least one adverse event defined as grade 3 or higher in severity was reported in 27% of patients who received lenzilumab compared with 33% who received placebo. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events of grade 3 severity or higher were related to respiratory (25% and 28%, respectively) and cardiac (6% and 5%, respectively) disorders. No deaths related to adverse events occurred.
“Lenzilumab significantly improved survival without invasive mechanical ventilation in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who were treated concurrently with other available therapies,” the researchers wrote. “However, the added value of lenzilumab beyond other immunomodulators used to treat COVID-19 alongside steroids remains to be confirmed.”
In September, Humanigen announced that the FDA declined its request for emergency use authorization (EUA) of lenzilumab in patients newly hospitalized with COVID-19. In its letter, the FDA said it was unable to conclude that the known and potential benefits of lenzilumab outweigh the known and potential risks of its use as a treatment for COVID-19, according to a company press release.
“We remain committed to bringing lenzilumab to patients hospitalized with COVID-19,” Cameron Durrant, MD, CEO of Humanigen said in the release. “We believe the ongoing ACTIV-5/BET-B trial, which has been advanced to enroll up to 500 patients, may provide additional safety and efficacy data sufficient to support our efforts to obtain an EUA to treat hospitalized COVID-19 patients.”
Reference:
FDA has declined Humanigen’s Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) Request for Lenzilumab in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Published Sept. 9, 2021. Accessed Dec. 15, 2021.
LIVE-AIR는 무작위 이중 블라인드 위약 조절 3상 실험으로, 침습적 기계적 인공호흡이 필요하지 않은 COVID-19 폐렴 성인 479명(평균 연령, 61세, 65% 남성)을 포함했다. 2020년 5월부터 2021년 1월까지 미국과 브라질의 29개 진료소에서 환자가 등록됐다. 환자들은 8시간 간격으로 IV 렌질루맙 600 mg(Humanigen; n = 236) 또는 위약(n = 243)을 3회 투여하도록 무작위로 할당되었다. 또한 모든 환자는 렘데시비르(Veklury, Giliad Science)와 코르티코스테로이드를 포함한 표준 보조 치료를 받았으며, 환자의 94%는 스테로이드, 72%는 렘데시비르, 69%는 둘 다 받았다.
주요 결과는 침습적 기계적 인공호흡 없이 28일 동안 생존하는 것이었다. 일차 결과는 위약을 투여받은 78%와 비교하여 렌질루맙을 투여받은 환자의 84%에서 달성되었다. (HR = 1.54; 95% CI, 1.02-2.32; P = .04)
침습적 기계적 인공호흡, 체외막 산소공급 또는 사망의 발생률은 위약 그룹의 21%(OR = 0.67, 95% CI, 0.41-1.1; P = 0.11)와 비교하여 렌질루맙 그룹의 15%에서 발생했다. 인공호흡기 없는 평균 일수는 레질루맙 그룹에서 8.8일, 위약 그룹에서 10.5일이었다(P = .077). 평균 ICU 체류는 렌질루맙 그룹의 경우 10일, 플라시보 그룹의 경우 11일이었다(P = .16).
기준에서 중앙 CRP는 79 mg/L(렌질루맙 그룹 77 mg/L, 플라시보 그룹 82 mg/L)이었다. 민감도 분석은 79 mg/dL 미만의 CRP 수준이 침습적 기계적 인공호흡 없이 생존할 수 있는 가장 큰 가능성과 관련이 있음을 보여주었다.
연구자들은 "이러한 탐색적 발견이 기준 CRP에 따라 질병 진행 초기에 단일 상류 사이토카인을 목표로 하는 치료 가능성을 나타낼 수 있다"고 썼다.
중증도 3등급 이상으로 정의된 최소 한 가지 부작용은 레질루맙을 받은 환자의 27%에서 보고되었으며 위약을 받은 환자의 33%에서 보고되었다. 중증도 3등급 이상의 가장 흔한 치료응급 부작용은 호흡기 질환(각각 25%, 28%)과 심장 질환(각각 6%, 5%)이었다. 부작용과 관련된 사망자는 발생하지 않았다.
연구자들은 "렌질루맙은 다른 이용 가능한 치료법과 병행 치료를 받은 COVID-19 입원 환자들에게 침습적인 기계적 인공호흡 없이 생존력을 크게 향상시켰다"고 썼다. "그러나, 스테로이드와 함께 COVID-19를 치료하기 위해 사용되는 다른 면역조절제들보다 렌질루맙의 부가 가치는 여전히 확인되어야 합니다."
지난 9월 후마니젠은 FDA가 COVID-19로 새로 입원한 환자에 대한 렌질루맙의 긴급사용허가(EUA) 요청을 거절했다고 발표했다. FDA는 서한에서 렌질루맙이 COVID-19 치료제로 사용될 경우 발생할 수 있는 위험성보다 더 큰 것으로 결론지을 수 없다고 밝혔다.
카메론 듀란트 후마니겐 최고경영자(CEO)는 "코로나바이러스로 입원한 환자들에게 렌질루맙을 전달하기 위해 노력하고 있다"고 밝혔다. "우리는 최대 500명의 환자를 등록하기 위해 진행 중인 ACTIV-5/BET-B 시험이 입원한 COVID-19 환자를 치료하기 위한 EUA를 얻기 위한 우리의 노력을 뒷받침하기에 충분한 추가적인 안전 및 효능 데이터를 제공할 수 있을 것으로 믿는다."
참조:
FDA는 입원 중인 COVID-19 환자에 대한 Lenzilumab에 대한 Humanigen의 긴급 사용 허가(EUA) 요청을 거절했습니다. 2021년 9월 9일 발행. 2021년 12월 15일 접속.
게시글 찬성/반대
- 0추천
- 0반대
운영배심원의견
운영배심원의견이란
운영배심원(10인 이하)이 의견을 행사할 수 있습니다.
운영배심원 4인이 글 내리기에 의견을 행사하게 되면
해당 글의 추천수와 반대수를 비교하여 반대수가
추천수를 넘어서는 경우에는 해당 글이 블라인드 처리
됩니다.

 Read next
Read next





댓글목록